In the silent architecture of the human body, bones stand as the unsung pillars, quietly supporting the grand design of life. Yet, beneath their sturdy facade, a hidden challenge lurks, one that can gradually erode their strength and resilience. While osteoporosis is often perceived as a condition that predominantly affects women, men are not immune to its silent encroachment. As the years progress, the risk of osteoporosis in men increases, subtly threatening their skeletal fortress. This article embarks on a journey to illuminate the pathways of prevention and management of osteoporosis in men, offering insights into safeguarding these vital structures. Through a blend of scientific understanding and practical guidance, we aim to equip men with the tools to fortify their bones and maintain their foundation for a lifetime of strength and vitality.
Understanding Osteoporosis in Men: A Silent Threat
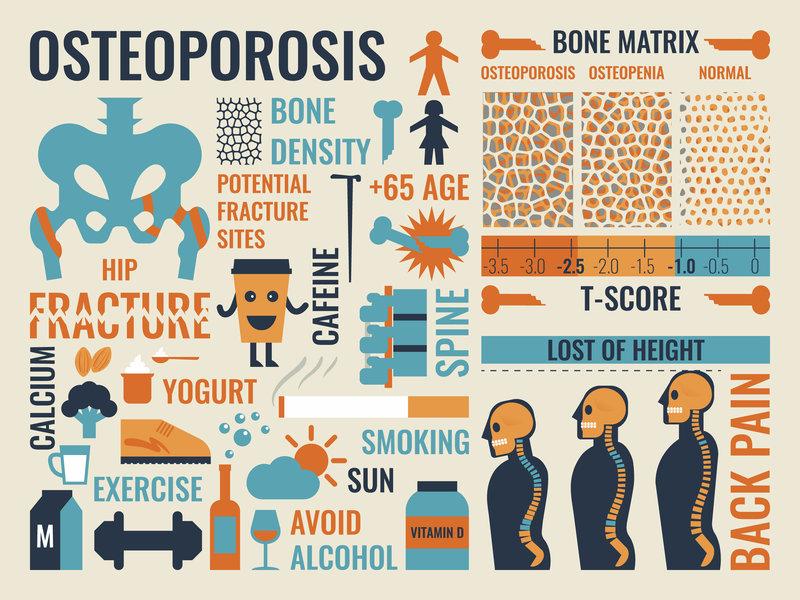
While osteoporosis is often perceived as a women’s health issue, it quietly impacts a significant number of men, particularly as they age. The condition, characterized by decreased bone density and increased fracture risk, can be managed effectively with proactive measures. Lifestyle adjustments play a crucial role in preventing and managing osteoporosis. Men should prioritize a balanced diet rich in calcium and vitamin D, engage in regular weight-bearing exercises like walking or resistance training, and avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption. Additionally, routine health check-ups to monitor bone density can aid in early detection and intervention.
- Calcium and Vitamin D Intake: Incorporate dairy products, leafy greens, and fortified foods into your diet.
- Exercise Regularly: Focus on activities that enhance bone strength and balance.
- Avoid Smoking and Limit Alcohol: These habits can accelerate bone loss.
- Regular Screening: Early diagnosis through bone density tests can help manage the condition effectively.
Furthermore, medical management might be necessary for those at higher risk or already diagnosed. Medications such as bisphosphonates, along with hormone-related therapies, can be discussed with healthcare providers to tailor a treatment plan. By understanding the silent nature of osteoporosis in men, individuals can take meaningful steps towards maintaining bone health and reducing the risk of fractures, thus ensuring a better quality of life as they age.
Lifestyle Choices: Building Stronger Bones through Diet and Exercise
Incorporating specific lifestyle changes can significantly enhance bone health and reduce the risk of osteoporosis in men. Diet plays a pivotal role in fortifying bones. Prioritize foods rich in calcium and vitamin D, as they are crucial for bone density. Consider integrating the following into your daily meals:
- Leafy green vegetables like kale and spinach
- Dairy products such as milk, cheese, and yogurt
- Fatty fish, including salmon and mackerel
- Nuts and seeds, particularly almonds and chia seeds
Equally important is a consistent exercise regimen that emphasizes weight-bearing and resistance activities. These exercises stimulate bone formation and improve balance, reducing fall risks. Aim to incorporate:
- Brisk walking or jogging
- Strength training with weights or resistance bands
- Balance exercises like tai chi or yoga
- Climbing stairs or hiking
Adopting these dietary and physical activity strategies can serve as a robust foundation for maintaining bone health and managing osteoporosis effectively.

Medical Interventions: Exploring Treatments and Therapies
Osteoporosis, often associated with women, also significantly impacts men, particularly as they age. Fortunately, several effective strategies can help prevent and manage this condition. Dietary choices play a crucial role; ensuring adequate intake of calcium and vitamin D is essential. Foods like dairy products, leafy greens, and fortified cereals can help maintain bone health. In addition to diet, regular weight-bearing exercises such as walking, jogging, or strength training can improve bone density and reduce the risk of fractures.
- Maintain a balanced diet rich in calcium and vitamin D.
- Engage in regular weight-bearing and muscle-strengthening exercises.
- Avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
- Consult healthcare providers for regular bone density tests.
- Consider medications if recommended by a healthcare professional.
Lifestyle modifications are also vital. Avoiding smoking and limiting alcohol consumption can prevent bone loss. Regular medical check-ups, including bone density tests, can help monitor bone health. In some cases, healthcare providers may recommend medications that slow bone loss and increase bone strength. By adopting these proactive measures, men can effectively manage their bone health and reduce the impact of osteoporosis.

Monitoring Bone Health: Regular Screenings and Self-Care Practices
Maintaining strong bones is crucial for men as they age, and incorporating regular screenings and self-care practices can play a pivotal role in this process. Bone density screenings are essential in identifying early signs of osteoporosis, allowing for timely intervention. It is recommended that men, especially those over 50 or with risk factors such as family history or lifestyle choices, consult with their healthcare providers to determine an appropriate screening schedule. These screenings provide valuable insights into bone health and can help in crafting a personalized management plan.
Beyond medical screenings, integrating self-care practices into daily life can significantly bolster bone health. Consider the following strategies:
- Balanced Nutrition: Ensure your diet includes sufficient calcium and vitamin D, vital for bone strength.
- Regular Exercise: Engage in weight-bearing and muscle-strengthening exercises to enhance bone density.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Limit alcohol intake and avoid smoking to reduce bone loss risk.
- Mindful Monitoring: Stay alert to any signs of bone weakness or fractures and seek medical advice promptly.
By adopting these practices, men can take proactive steps in monitoring and preserving their bone health, ultimately reducing the risk of osteoporosis and its associated complications.








