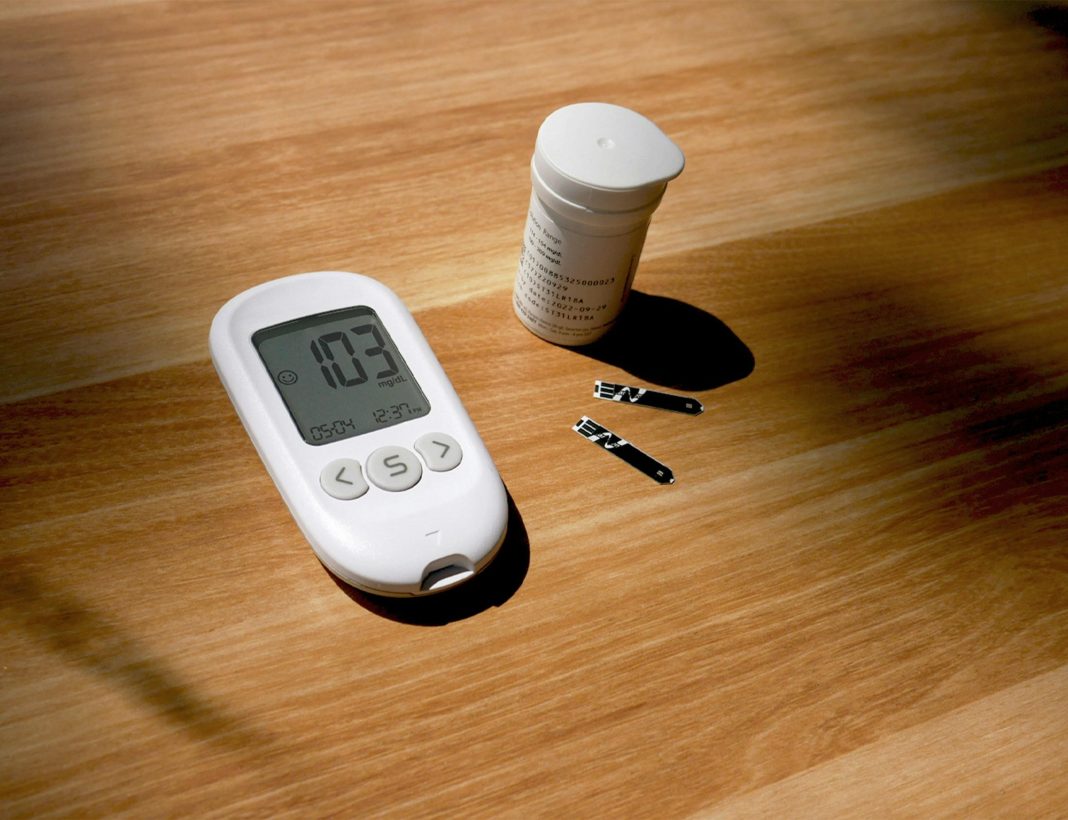
In the delicate dance of managing diabetes, precision is paramount. At the heart of this intricate choreography lies a seemingly simple device: the blood sugar monitor. This small, often understated gadget holds the power to illuminate the invisible fluctuations of glucose within the bloodstream, offering a semblance of control in the face of an unpredictable condition. Yet, as technology advances and new devices flood the market, a pressing question emerges from the shadows: Are these blood sugar monitors truly accurate? This article delves into the science, the skepticism, and the subtle nuances of these critical tools, exploring their role in the ever-evolving landscape of diabetes management. Join us as we unravel the truth behind the numbers, navigating the intersection of innovation and reliability.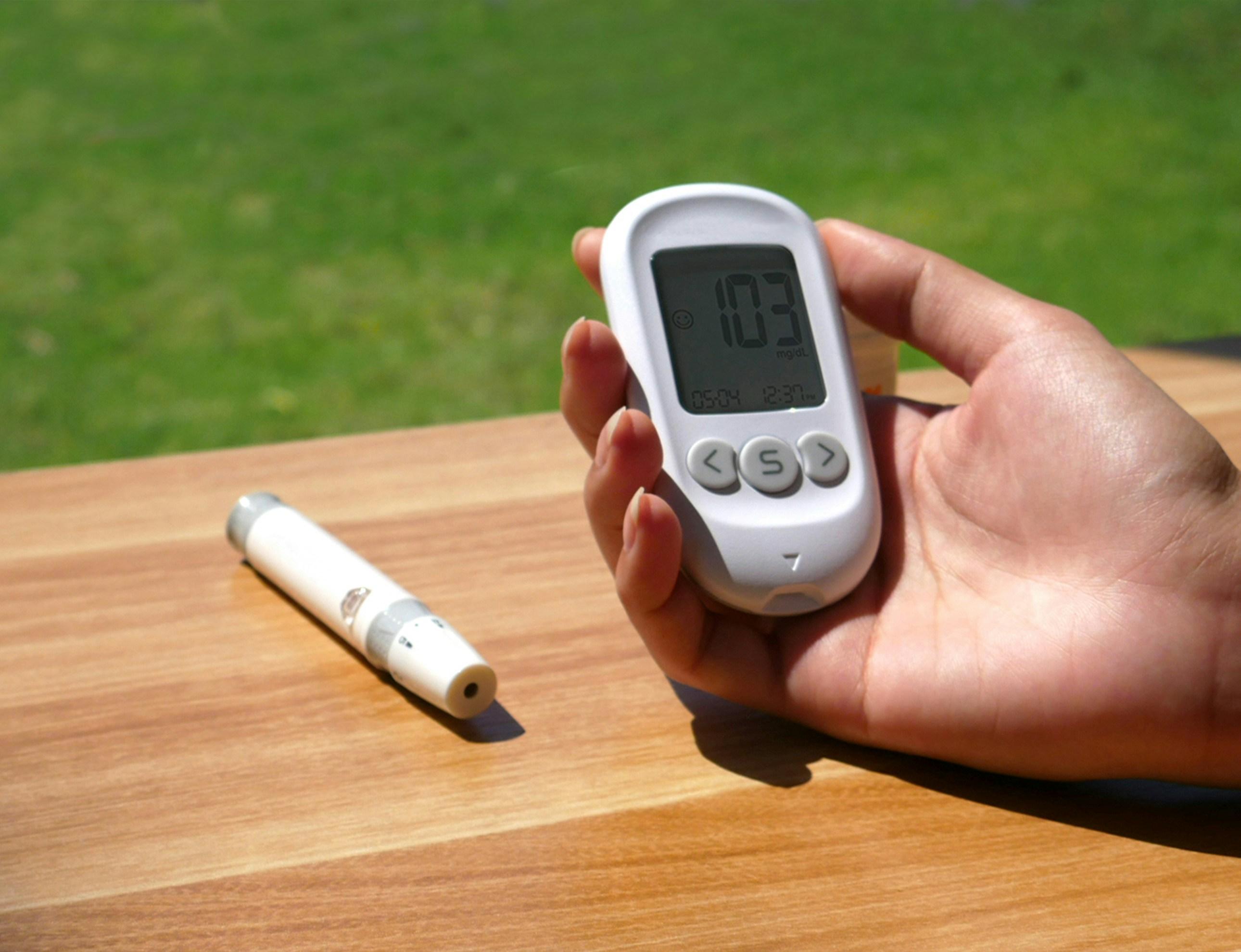
Understanding the Science Behind Blood Sugar Monitors
Blood sugar monitors, often hailed as vital tools for diabetes management, operate on intriguing scientific principles. At their core, these devices utilize electrochemical technology. A small drop of blood placed on a test strip enters a reaction chamber where glucose oxidase, an enzyme, interacts with glucose molecules. This interaction generates an electrical current proportional to the glucose concentration, which the monitor then translates into a readable glucose level.
While the science is robust, several factors can affect the accuracy of these readings. User error, such as incorrect calibration or expired test strips, can skew results. Environmental conditions, like temperature and humidity, might also play a role. Additionally, physiological factors, such as dehydration or high hematocrit levels, can influence readings. Despite these variables, modern blood sugar monitors are designed to minimize inaccuracies, offering a reliable snapshot of blood glucose levels for informed diabetes management.

Evaluating Accuracy: Factors That Influence Blood Sugar Readings
Several factors can influence the accuracy of blood sugar readings, potentially impacting diabetes management. Understanding these elements is crucial for anyone relying on glucose monitors to maintain optimal health. One of the primary considerations is calibration. Devices require regular calibration to ensure that the readings reflect true blood glucose levels. An incorrectly calibrated device can lead to misleading results, which may affect treatment decisions.
Environmental factors also play a significant role. Temperature and humidity levels can interfere with the chemical reactions in test strips, leading to inaccurate readings. User error is another common issue; improper use of the device, such as not washing hands before testing or using expired test strips, can skew results. Additionally, physiological variations such as hematocrit levels (the proportion of red blood cells in the blood) can affect the accuracy of readings. It is essential to be aware of these influences to ensure that blood sugar monitors provide reliable data.
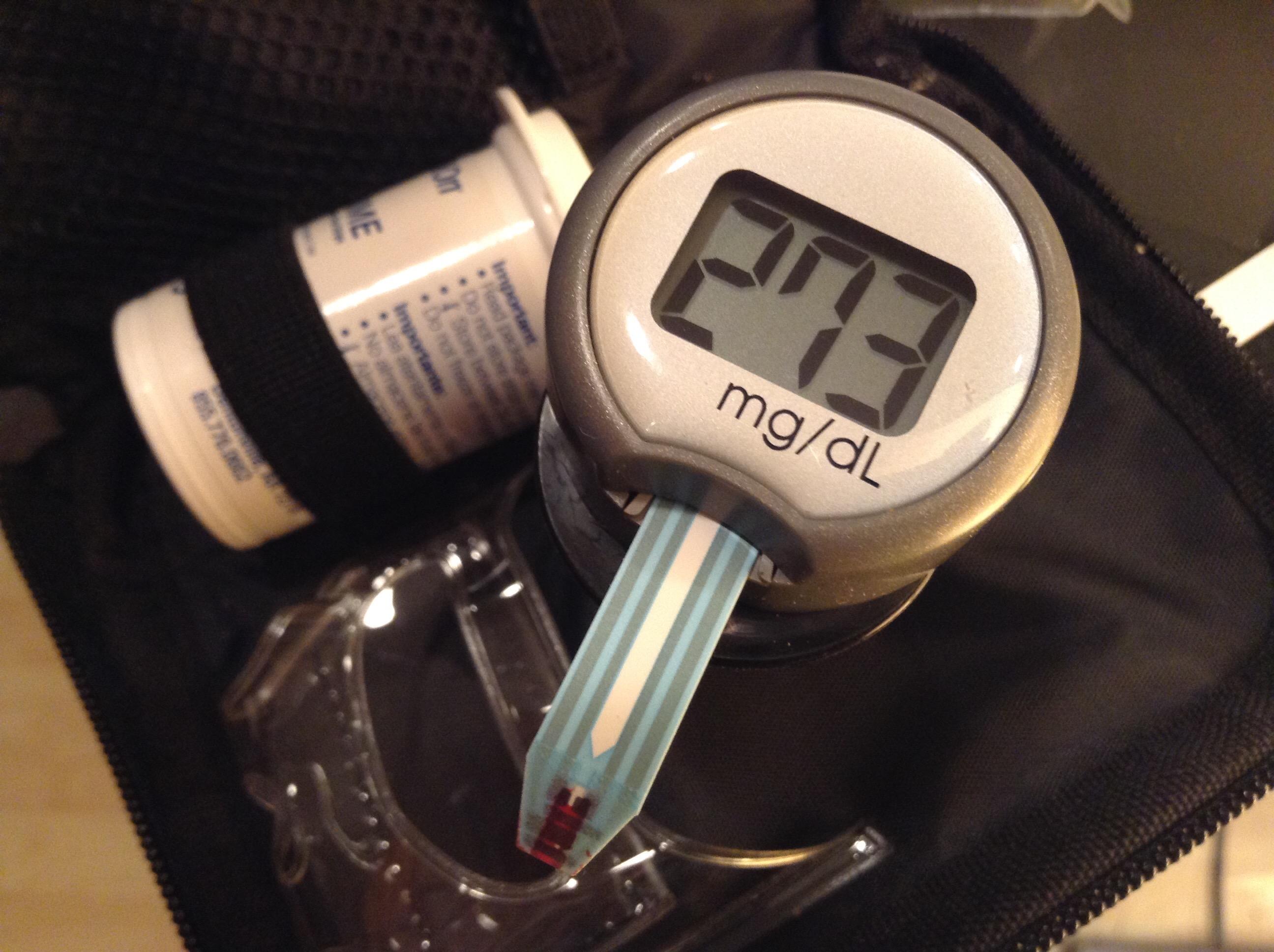
Comparing Different Types of Blood Sugar Monitoring Devices
When it comes to managing diabetes, selecting the right blood sugar monitoring device is crucial. There are several types of devices available, each with its own set of features and benefits. Traditional glucometers are widely used and require a small blood sample from a finger prick. They provide results in seconds and are generally reliable, though some users find the need for frequent testing cumbersome. On the other hand, continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) offer a more comprehensive overview by tracking glucose levels throughout the day and night. They are typically worn on the body and can alert users to highs and lows without the need for constant manual testing.
- Traditional Glucometers: Require finger pricks, immediate results, cost-effective, may require calibration.
- Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs): Provide ongoing data, less invasive after initial setup, more expensive, require a sensor change every 7-14 days.
Another option includes flash glucose monitoring systems, which allow users to scan a sensor with a reader or smartphone to get a glucose reading. While similar to CGMs, they do not offer real-time alerts, which might be a downside for some users. Ultimately, the choice between these devices depends on personal preference, lifestyle, and specific medical needs. Consulting with healthcare professionals can aid in making the best choice for effective diabetes management.
Expert Recommendations for Optimizing Diabetes Management
In the realm of diabetes management, ensuring the accuracy of blood sugar monitors is crucial. While these devices are generally reliable, experts recommend a few strategies to enhance their effectiveness. Firstly, regular calibration of your device is essential. This ensures that your readings are as accurate as possible, which can help in making informed decisions about your health. Additionally, it is important to use test strips correctly. Ensure they are stored properly and are not expired, as this can significantly affect the readings.
Experts also suggest maintaining a consistent testing routine. Checking your blood sugar at the same times each day can provide a more comprehensive view of how your levels fluctuate. Furthermore, consider keeping a detailed log of your readings, including notes on meals, exercise, and any stress factors, to identify patterns and triggers. if discrepancies or unusual readings occur, it may be beneficial to consult with a healthcare professional to verify the monitor’s accuracy or explore alternative monitoring options.